MATHEMATICS
Logarithm Rules
The base b logarithm of a number is the exponent that we need to raise the base in order to get the number.Logarithm definition
When b is raised to the power of y is equal x:
b y = x
Then the base b logarithm of x is equal to y:
logb(x) = y
For example when:
24 = 16
Then
log2(16) = 4
Logarithm as inverse function of exponential function
The logarithmic function,
y = logb(x)
is the inverse function of the exponential function,
x = by
So if we calculate the exponential function of the logarithm of x (x>0),
f (f -1(x)) = blogb(x) = x
Or if we calculate the logarithm of the exponential function of x,
f -1(f (x)) = logb(bx) = x
Natural logarithm (ln)
Natural logarithm is a logarithm to the base e:
ln(x) = loge(x)
When e constant is the number: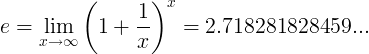
or
Inverse logarithm calculation
The inverse logarithm (or anti logarithm) is calculated by raising the base b to the logarithm y:
x = log-1(y) = b y
Logarithmic function
The logarithmic function has the basic form of:
f (x) = logb(x)
